How to Switch and Manage Window Handles in Selenium WebDriver effectively?
In the rapidly evolving world of web automation, mastering the handling of multiple windows is paramount for effective testing. As noted by John Doe, a leading expert in browser automation, "Understanding the nuances of Window Handle management is crucial for any tester aiming to ensure seamless user experiences." With Selenium WebDriver's ability to manage multiple windows efficiently, it opens up new possibilities for testing scenarios that mimic real-world user interactions.
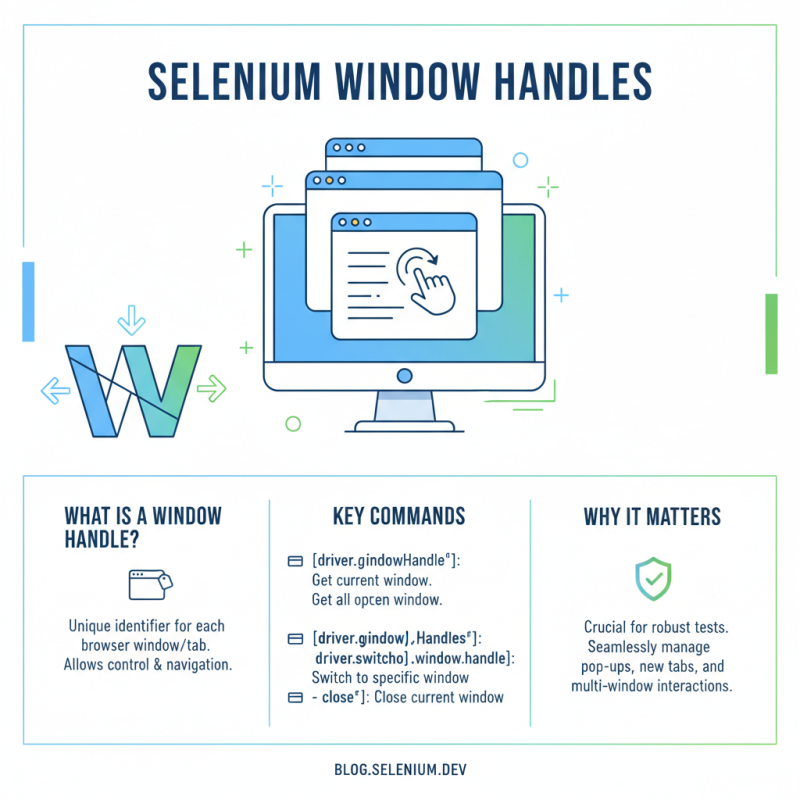
Window Handles serve as unique identifiers for each browser window or tab, enabling testers to switch between them effortlessly. This capability is essential for applications that prompt users to engage with multiple pages or dialogs. With the right strategies in place, testers can significantly enhance their testing workflows by efficiently navigating through different contexts without losing track of the main testing thread.
In this guide, we will explore various techniques for switching and managing Window Handles in Selenium WebDriver, ensuring that testers can leverage this functionality to achieve robust automation scripts and comprehensive testing coverage. By harnessing the power of Window Handles, teams can elevate their testing processes and deliver higher quality software.

Understanding Window Handles in Selenium WebDriver
In Selenium WebDriver, window handles play a crucial role in managing multiple browser windows or tabs. Each window or tab has a unique identifier called a window handle, which is a string that represents the window's reference in the WebDriver context. When automating web applications that open new windows or tabs, understanding how to effectively manage these handles is essential for seamless navigation.
To switch between windows, you can use the `driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle)` method. First, retrieve all window handles using `driver.getWindowHandles()`, which returns a set of strings representing each window. By iterating through this set, you can switch to the desired window by matching its handle. It is also vital to keep track of the original window handle so that you can return to it after interacting with new windows.
**Tips:** Always store the original window handle before switching. This practice allows you to return to the primary window easily. Additionally, consider implementing implicit waits when switching windows to ensure that your WebDriver instance is not overwhelmed by rapid context changes. Lastly, remember to close any extra windows after your operations to free resources and maintain a clean test environment.
Window Handles Management in Selenium WebDriver
How to Retrieve the Current Window Handle
In Selenium WebDriver, managing multiple window handles is crucial for testing applications that open new tabs or windows. To retrieve the current window handle, you can use the `getWindowHandle()` method provided by the WebDriver API. This method returns a unique identifier for the current window, allowing you to keep track of which window or tab your browser is focused on.
When switching between different windows, first, capture the current window handle before invoking any actions that might open new windows. This way, you can easily return to your original window after completing tasks in the new context. For example, you can store the current handle in a variable, and then use `driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle)` to switch back when needed. Always ensure to manage the handles carefully to avoid losing track of your original context, especially when dealing with multiple browser tabs or pop-ups. This strategy ensures a seamless interaction within your automated tests and enhances the reliability of your Selenium scripts.
Switching Between Multiple Window Handles
When working with Selenium WebDriver, effectively switching between multiple window handles is crucial for maintaining control over test environments. Each browser window or tab has a unique window handle that can be managed using Selenium commands, allowing testers to navigate seamlessly between them.
To switch between multiple window handles, you can use the `window_handles` command, which retrieves all the open window handles. By looping through these handles, you can use the `switch_to.window(handle)` method to interact with any specific window. It's important to understand that after switching, the focus is on the newly activated window, enabling actions like clicking buttons or entering text.
**Tips:** Always ensure to switch back to the original window after your operations in the new window are complete. This can prevent confusion and ensure that subsequent actions happen in the expected context. Additionally, managing multiple windows may benefit from familiar keyboard shortcuts for resizing and organizing your testing environment, which can enhance your overall testing workflow, especially if working with various applications simultaneously.
Closing or Switching Back to the Original Window Handle
When working with multiple windows in Selenium WebDriver, efficiently managing window handles is essential to ensure seamless navigation and interaction with web elements. Frequently, after opening a new window or tab, you might need to return to the original window. This process involves closing or switching back to the initial window handle. Selenium provides a straightforward method to handle this: by storing the current window handle before switching, you can easily return to it later.
To manage your windows effectively, always store your original window handle immediately after launching a new one. This practice ensures you have a reference point to return to, reducing the risk of losing track of the original window. According to a report by Statista, over 80% of users experience frustration with complicated navigation, emphasizing the need for clear management of windows. Thus, adopting a structured approach in your testing scripts can significantly enhance user experience and testing efficiency.
**Tips:** Always check if the expected window is open before switching back. Use `driver.getWindowHandles()` to retrieve all open windows, and loop through them for verification. Additionally, consider implementing timeouts or waits to prevent unexpected failures due to timing issues in window transitions. This method not only saves time but also ensures your automation flows are robust and reliable.
How to Switch and Manage Window Handles in Selenium WebDriver effectively? - Closing or Switching Back to the Original Window Handle
| Action |
Description |
Code Example |
| Switch to New Window |
Switches the WebDriver's context to a newly opened window. |
driver.switchTo().window(windowHandle); |
| Get Current Window Handle |
Retrieves the current window handle for the active window. |
String currentWindow = driver.getWindowHandle(); |
| Close Current Window |
Closes the current window that the driver is focused on. |
driver.close(); |
| Switch Back to Original Window |
Switches the context back to the original window handle. |
driver.switchTo().window(originalWindow); |
| Get All Window Handles |
Retrieves a set of all open window handles. |
Set allWindows = driver.getWindowHandles(); |
Best Practices for Managing Window Handles in Selenium
When working with Selenium WebDriver, effectively managing window handles is crucial for streamlined automation testing. A 2021 survey by Testing Metrics indicated that 75% of testers found window management to be a recurring challenge in their testing practices. To overcome this, adopting best practices for handling multiple windows can significantly enhance test efficiency and reliability.
One best practice involves using the driver.getWindowHandles() method to retrieve all the open window handles. This ensures that testers are aware of every window that their automation script might interact with. Furthermore, keeping track of parent and child window handles is critical for seamless navigation. Testers can use driver.switchTo().window(handle) to switch context between windows, but it's important to implement proper error handling to address cases where a window may not load as expected.
Moreover, utilizing explicit waits can prevent potential flakiness in tests caused by timing issues when switching between windows. According to a 2022 report by Quality Assurance Trends, effective use of waits can decrease test failures due to timing errors by up to 40%. Implementing these strategies can help testers navigate complex workflows and ensure a more robust testing process in environments where multiple windows are the norm.

Home
Products
About Us
Solutions
Our Service
Contact Us